[LeetCode] 108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Problem
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1:

Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:

Example 2:
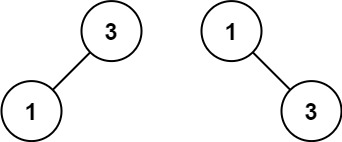
Input: nums = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
Solution
Logic
-
배열의 중앙에 위치하는 요소가 배열의 Root 노드의 값이 되므로 전체 배열에서 중앙에 위치하는 요소를 Root 노드의 값으로 만든다.
-
배열 내에서 Root 노드의 값에 해당하는 요소의 좌측 배열과 우측 배열 각각 중앙에 위치한 요소가 Root 노드의 좌측, 우측 자식 노드의 값이 된다.
-
위 과정을 반복하되, 배열의 범위를 벗어나는 요소를 참조하려 하거나 이미 참조한 요소를 다시 참조하려는 경우 반복을 중단한다.
Code
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) { TreeNode root = buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1); return root; } private TreeNode buildTree(int[] nums, int left, int right) { // left, right는 배열 속 인덱스 if (right < left) return null; // right < left 일 때 배열의 범위를 벗어난 요소를 참조하거나 참조했던 요소를 다시 참조하는 꼴 int center = (left + right) / 2; TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[center]); node.left = buildTree(nums, left, center - 1); node.right = buildTree(nums, center + 1, right); return node; } }Time Compexity
Leave a comment